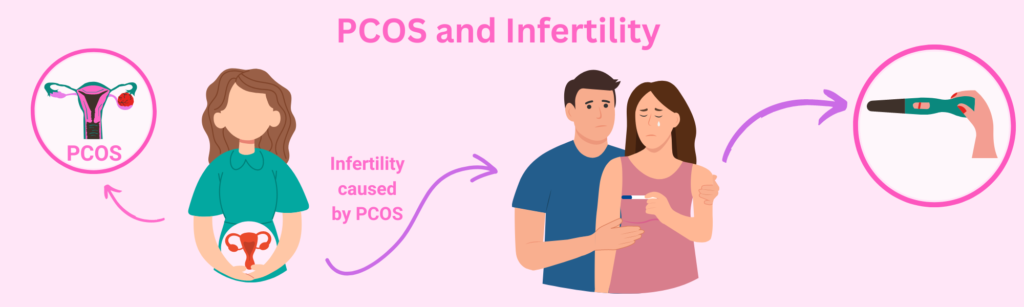
PCOS can be simply understood as being directly linked with infertility because the PCOS ovulation process itself is improper, which hinders the ovary from getting the desired level of hormone necessary for ovulation. It leads to irregular periods and also causes infertility.
Some women with PCOS may release mature eggs occasionally, but in others there is a complete absence of ovulation. To conceive, fertilization takes place between sperm and a mature egg; ovulation becomes the primary requirement to get pregnant.
PCOS & Pregnancy
Women with PCOS have difficulty conceiving as well as an increased risk of complications during pregnancy. The majority of females with PCOS become pregnant; they take longer to get pregnant and often need fertility treatment in comparison to women without PCOS.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a healthy weight range, a healthy diet, regular exercise, no smoking or drinking, enough sleep, and a stress-free environment, increases the chances of pregnancy and having a healthy baby.
For overweight women with PCOS, modest weight loss in some cases, lead to regular ovulation.
When Should You Seek Medical Help?
Seek medical advice when you tried for a baby for 12 months without success ,if age above 35 time window decreases to six months.
In case of sporadic or irregular periods, an indication that ovulation is not taking place and needs medical help to get pregnant. The first line of treatment is ovulation induction, which involves a course of tablets or injections to stimulate the ovary for the release of an egg that can be fertilized either during intercourse or through IUI.
If none of the above methods work, a more invasive method such as IVF is required.
The IVF procedure includes a number of injections to stimulate the ovary for the production of multiple eggs. Once mature, the eggs are retrieved in an ultrasound-guided procedure, and sperm is added for the lab formation of embryos.
After a few days, the embryo is placed in the uterus, where it may implant and grow into a baby. In an IVF procedure, there are more chances that two embryos, or womb embryos,wembryos,can be frozen for later use if there is no pregnancy.
Beware of some possible health effects like ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, which is an overreaction to fertility drugs used to stimulate the ovaries for the production of multiple eggs. It can lead to nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, blood clots, and rapid weight gain.
Pregnancy Complications in PCOS:
It includes preeclampsia (a condition in pregnancy characterized by high blood pressure, sometimes with fluid retention and proteinuria), which is dangerous for both mother and fetus. Other complications include pregnancy-induced hypertension (high blood pressure) and gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes can lead to having a larger-than-average baby, which may cause complications during delivery like shoulder dystocia (when the baby’s shoulder gets stuck during labor).
Most PCOS symptoms during pregnancy are treatable with careful monitoring. In cases of gestational diabetes, insulin may be required to maintain blood sugar levels.
PCOS Treatment –
Treatment of PCOS depends on various factors and differs from individual to individual. Some factors are age, symptoms, and overall health; it also depends on whether one is willing to get pregnant or not.
If one is planning to get pregnant, possible treatment options are:
- Lifestyle Change
- Dietary modification
- Ovary stimulation with use of medication
- Invasive treatment like IVF
- If pregnancy is not a concern:
- Birth control pills
- Diabetes medication
- A change in lifestyle and diet
- Medications for symptoms – specific medications for symptom relief like acne or hair loss etc.